Supply Chain Optimization
Inbound vs Outbound Logistics: Key Differences in 2025
May 30, 2025
14 mins read

Key Takeaways
- Inbound logistics manages raw materials from suppliers to production facilities, while outbound logistics handles finished products to customers, requiring distinct optimization strategies for each flow.
- Efficient logistics operations directly impact customer satisfaction, with one-third of customers willing to abandon a brand after a single poor delivery experience.
- Technology adoption and process automation are critical for optimizing both inbound and outbound logistics, yet 67.4% of supply chain managers still rely on basic spreadsheets.
- Locus’ Dispatch Management Software streamlines both logistics flows through real-time tracking, route optimization, and automated order processing, enabling cost reduction and improved delivery accuracy.
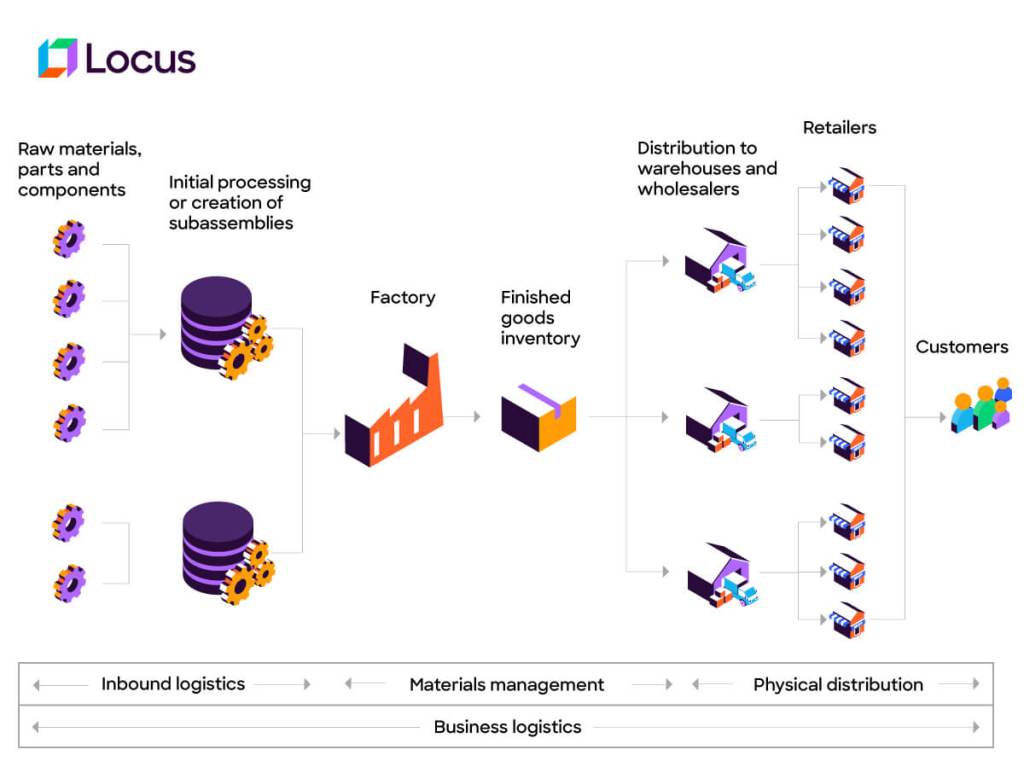
In the vast, interconnected world of supply chain management, two terms often come into focus—inbound and outbound logistics. Both are crucial elements of a well-functioning supply chain, yet they serve different purposes and face unique challenges. In this post, we deep dive into the world of inbound and outbound logistics, dissecting their key differences, their significance in the broader spectrum of supply chain operations, and their critical role in the last mile of delivery.
Inbound and outbound logistics are two fundamental components of the overall supply chain management process. They involve the movement and management of goods and materials, but their directions and specific functions differ from each other. Here’s an explanation of both:
What Is Inbound Logistics?
Inbound logistics refers to the activities involved in receiving, storing, and distributing raw materials, components, and other inputs needed for production or further processing within a company. It focuses on managing the flow of materials from suppliers or vendors to the company’s production facilities. Inbound logistics activities typically include transportation, warehousing, inventory control, material handling, quality control inspections, and scheduling.
The main objectives of inbound logistics are to ensure timely and efficient delivery of materials to support production processes, optimize inventory levels, minimize costs associated with transportation and storage, and maintain good relationships with suppliers. Effective inbound logistics management helps streamline production operations and reduce supply chain disruptions.
What Is Outbound Logistics?
Outbound logistics deals with activities relating to the movement and management of finished products or goods from the company’s production facilities to the end customers or distribution channels. It focuses on delivering the final products or services to the intended recipients.
Outbound logistics activities include order processing, packaging, storage, transportation, distribution channel management, and customer support. The primary goals of outbound logistics are to ensure accurate and timely delivery of products, optimize transportation and distribution processes, minimize costs, manage inventories in distribution centers or warehouses, and provide excellent customer service.
Difference Between Inbound and Outbound Logistics
The key difference between inbound and outbound logistics lies in the direction of the flow of goods. Inbound logistics deals with the movement of materials and inputs from suppliers to the company, while outbound logistics deals with the movement of finished products from the company to customers or distribution channels.
| Inbound Logistics | Outbound Logistics | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of managing and controlling the flow of raw materials, goods, and supplies from suppliers to the organization’s facilities. | Managing and controlling the flow of finished products from the organization’s facilities to the end customers or distribution centers. |
| Focus | Procurement, receiving, storage, and inventory management. | Order processing, fulfillment, transportation, and delivery. |
| Activities | Tasks such as supplier management, procurement planning, order placement, transportation coordination, receiving and inspection, warehousing, and inventory management. | Activities such as order management, order picking and packing, transportation planning and coordination, delivery route optimization, shipment tracking, and customer service. |
| Objective | Ensure the timely and efficient delivery of raw materials and supplies to support production or further processing within the organization’s facilities. | Ensure the accurate and timely delivery of finished products to the intended recipients, meeting customer demands and expectations |
Importance of Efficient Inbound and Outbound Logistics
Efficient inbound and outbound logistics play a crucial role in any business, especially in manufacturing, retail, and e-commerce, where supply chains are central to operations. Both inbound (receiving goods) and outbound (sending goods) logistics encompass the management of materials and finished products, ensuring that operations run smoothly. Here are some key reasons that illustrate their importance:
1. Cost-effectiveness: An efficient logistics system can significantly reduce costs related to storage, transportation, and handling of goods. Efficient supply chain management can result in significant savings, improving a company’s profit margin.
2. Customer Satisfaction: For many businesses, the end goal of outbound logistics is delivering a product to a customer. Quick, efficient, and accurate deliveries can significantly enhance customer satisfaction. In the era of e-commerce, where next-day or even same-day delivery is becoming the norm, efficient logistics is critical to remaining competitive.
3. Inventory Management: Inbound logistics play a critical role in inventory management. Timely and reliable delivery of raw materials or components ensures that production processes can continue without interruption, which helps to prevent stockouts and backorders.
4. Operational Efficiency: Efficient logistics processes allow smooth operations, reduce lead times, and enhance productivity. They also help in managing the fluctuation of demand and supply effectively.
5. Competitive Advantage: Companies that have mastered their logistics can often provide better service than their competitors. This could mean faster delivery times, lower prices, or better customer service, which can be significant competitive advantages.
6. Sustainability: Efficient logistics also have an environmental impact. Companies can lower their carbon footprint by optimizing delivery routes and reducing waste in the supply chain.
7. Risk Management: Effective logistics management allows companies to anticipate and mitigate risks associated with transportation delays, supplier issues, or unexpected changes in demand.
Inbound and outbound logistics share some common challenges, while also presenting unique complexities. Here are some expanded insights into the challenges associated with both inbound and outbound logistics:
Challenges in Inbound Logistics
1. Supplier coordination: Coordinating with multiple suppliers to ensure timely delivery of raw materials and components can be a complex task, requiring effective communication and strong supplier relationships.
2. Inventory management: According to this report 67.4% of supply chain managers use Excel spreadsheets as a management tool. Balancing inventory levels to meet production demands while minimizing carrying costs and stockouts can be challenging. Accurate demand forecasting and efficient inventory control systems are vital.
3. Transportation and freight costs: Selecting the most cost-effective and reliable transportation modes and carriers for inbound shipments is crucial. Fluctuating fuel prices, capacity constraints, and changing regulations can impact transportation costs.
4. Warehouse efficiency: Effectively organizing and managing warehouses to receive, store, and handle incoming materials requires efficient layout design, optimized storage methods, and streamlined processes.
5. Quality control: Ensuring the quality of inbound materials is crucial to maintain product standards. Implementing rigorous inspection processes and supplier quality management systems is essential.
Challenges in Outbound Logistics
1. Order fulfillment: Managing and fulfilling customer orders accurately and efficiently can be complex, especially when dealing with a high volume of orders and diverse product SKUs.
2. Distribution network optimization: Designing an optimal distribution network that balances proximity to customers, transportation costs, and service levels is challenging. Factors such as warehouse locations, transportation routes, and inventory allocation must be considered.
3. Customer service and satisfaction: According to a survey by PwC, 1 in 3 customers would leave a brand they love after just one bad experience. Efficient outbound logistics is crucial for providing positive customer experiences, especially in terms of delivery time and accuracy. Meeting customer expectations for on-time delivery, order accuracy, and overall service excellence is critical. Maintaining a robust customer service system and addressing customer inquiries and concerns promptly is vital.
4. Last-mile delivery: The final stage of the delivery process can present challenges such as route optimization, traffic congestion, and managing multiple delivery time windows.
5. Returns and reverse logistics: Handling product returns, managing reverse logistics, and implementing efficient product recall processes can be demanding. Proper disposal, refurbishment, or restocking of returned products need to be managed effectively. The complexity of returns and reverse logistics shouldn’t be underestimated.
Key Steps in Inbound and Outbound Logistics Process
Inbound and outbound logistics shape how well a supply chain performs. Inbound moves the right materials into the organisation on time, while outbound moves finished goods to customers without delays. Together, they determine how well a business controls cost, speed, and service quality.
Here’s a step-by-step, side-by-side breakdown.
| Inbound Logistics Steps | Outbound Logistics Steps |
|---|---|
| 1. Sourcing Materials Selecting suppliers based on cost, quality, and reliability protects production schedules and reduces supply disruption. Strong sourcing prevents stockouts and stabilises long-term fulfilment. | 1. Order Processing Capturing and validating customer orders early prevents mis-shipments and delays. Clean order data improves fulfilment speed and reduces correction work downstream. |
| 2. Purchasing and Order Confirmation Placing and verifying purchase orders with clear documentation prevents quantity mismatches and freight disputes. Accurate confirmations shorten lead cycles and reduce rework. | 2. Picking and Packing Accurate picking and secure packing reduce returns, errors, and carton wastage. Clean execution at this stage supports faster hand-offs to carriers. |
| 3. Transportation and Freight Coordination Planning inbound freight with air, ocean, or road transport and using TMS systems improves cost control and visibility. Better freight coordination reduces dwell time and inbound bottlenecks. | 3. Transportation Planning and Dispatching Assigning shipments to vehicles and scheduling dispatch with route planning tools increases drop density and reduces idle miles. AI-based route planning can cut last-mile cost by up to 35% in dense urban areas. |
| 4. Receiving and Inspection Verifying goods against purchase orders at the dock reduces downstream quality failures. Fast exception reporting shortens recovery time for damaged or missing items. | 4. Shipping and Delivery Executing final-mile delivery with live status updates supports SLA control and reduces failed delivery attempts. Tracking protects service reliability in the last mile. |
| 5. Warehousing and Storage Placing goods in the right storage zones and maintaining stock accuracy improves retrieval speed and lowers carrying cost. A well-managed WMS supports clean hand-offs to production or outbound teams. | 5. Customer Communication and Support Proactive updates, proof of delivery, and quick issue handling build trust and reduce churn. Many customers stop buying after a poor delivery experience. |
| 6. Reverse Logistics Handling supplier returns and recycling with structured flows reduces waste and protects margin. Reverse efficiency also improves compliance on damaged or rejected inputs. | 6. Returns and Reverse Logistics Managing returns and replacements with clear rules shortens credit cycles and protects customer satisfaction. Clean reverse flows reduce friction in after-delivery service. |
Using a single platform like Locus to connect inbound and outbound flows gives clarity across the chain, reduces cost leakages, and improves delivery precision.
Top 10 Challenges in Inbound-Outbound Logistics Process
From visibility gaps and rising logistics costs to poor fleet productivity, inefficient in-plant operations, and fragmented systems, logistics teams face multiple hurdles that disrupt supply chain performance.
Below are the ten most critical challenges shaping inbound and outbound logistics today.
1. Limited Visibility Across Shipments
Poor visibility into inbound shipments and outbound deliveries makes it hard to track status or anticipate delays. Without real-time tracking and exception alerts, coordination between suppliers, carriers, and customers suffers.
2. Rising Logistics Costs
Fuel price swings, fragmented carrier networks, and weak route planning continue to push transportation costs up. For many companies, logistics is one of the largest cost centers in the supply chain, with transportation, warehousing, and last-mile execution accounting for a major share of total spend.
3. Inefficient In-Plant Operations
Unorganized warehouse layouts, manual inventory handling, and material mismanagement slow down both inbound receipt and outbound dispatch, increasing cycle times and costs.
4. Poor Fleet Productivity
Poor routing, idle time, and inconsistent driver output reduce delivery throughput. Automating dispatch and route planning helps increase vehicle use and overall delivery output.
5. Lack of Data-Driven Decision-Making
Many teams still rely on spreadsheets and disconnected systems, which limits performance insight. A 2024 KPMG report found that only half of supply chain organizations planned to invest in AI and advanced analytics that year — leaving the other half without data-driven capability.
6. Supplier and Carrier Coordination Gaps
Managing multiple vendors without shared visibility or digital collaboration often causes delayed raw material arrivals and late order fulfillment.
7. Fluctuating Demand and Forecast Inaccuracy
Sudden changes in demand or poor forecasting lead to stockouts or overstocking. Both strain inbound sourcing and outbound delivery schedules.
8. Last-Mile Delivery Inefficiencies
Traffic congestion, failed deliveries, and rigid delivery windows make outbound logistics unpredictable. Intelligent route optimization helps reduce these disruptions.
9. Sustainability Pressures
Customers and regulators now expect greener operations. Meeting emission-reduction goals requires rethinking routing, packaging, and reverse logistics processes.
10. Fragmented Technology Ecosystems
Disconnected WMS, TMS, and ERP systems make it difficult to share real-time information across departments. A unified dispatch management platform like Locus integrates these workflows, enabling end-to-end visibility and smarter decision-making.
How to Optimize Inbound and Outbound Logistics
Businesses optimize inbound and outbound logistics through various methods, many of which are tied to logistics planning, technological integration, process refinement, and supplier relationships. Here are some specific ways companies optimize these crucial aspects of their operations:
- Streamlining Processes: Regularly reviewing and refining processes can enhance efficiency in moving goods in and out.
- Technology Investment: Tools like Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Transportation Management Systems (TMS), and AI can optimize logistics operations.
- Supplier Collaboration: Building good relationships with suppliers ensures a smoother, more reliable supply of goods.
- Training: Staff training on best practices can reduce errors and boost efficiency.
- Just-In-Time Inventory: This approach minimizes inventory costs and relies on efficient inbound logistics.
- Demand Forecasting: Anticipating customer demand helps manage logistics, avoiding stock outs and overstocking.
- Automation: Automating logistics processes can improve speed and accuracy.
- Route Optimization: Efficient routing reduces delivery times and fuel costs for outbound logistics.
- Performance Measurement: Using key performance indicators (KPIs) helps identify areas for improvement.
- Risk Management: Contingency plans ensure business continuity when disruptions occur in the supply chain.
Optimizing inbound and outbound logistics requires a comprehensive, strategic approach that is continually adjusted as business needs, market conditions, and technologies evolve.
Simplify Inbound and Outbound Logistics with Intelligent Dispatch Management
Utilizing advanced software like Locus’ Dispatch Management Software not only enhances both inbound and outbound logistics but also promotes cost-effectiveness and customer satisfaction.
Inbound logistics are bolstered with seamless supplier coordination and real-time shipment visibility, ensuring timely raw material deliveries. This solution further optimizes warehousing, promoting efficient stock replenishment and reducing holding costs.
For outbound logistics, order processing becomes automated, enhancing speed and accuracy while reducing manual errors. Advanced route optimization software helps businesses minimize fuel costs and delivery time. The solution provides real-time tracking and communication, guaranteeing punctual deliveries and customer satisfaction.
Dispatch management’s key feature is last-mile optimization. Dynamic route planning, load matching, and real-time tracking capabilities account for variables like traffic and specific customer requirements. This ensures optimal resource utilization, reduces empty miles, and provides customers with accurate ETAs, promoting smooth deliveries and coordination.
By leveraging a dispatch management solution, businesses can optimize their inbound and outbound logistics operations, enhance the last mile delivery process, and achieve improved efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction in this dynamic market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the key difference between inbound and outbound logistics?
Inbound logistics deals with managing the flow of raw materials, components, and supplies from suppliers into the company’s production facilities. Outbound logistics focuses on the movement of finished goods from the company to customers or distribution channels. The primary difference lies in the direction of material/product flow – inbound brings in inputs for production, while outbound ships out final products after production.
What are some major challenges in inbound logistics?
Some key challenges in inbound logistics include coordinating with multiple suppliers for timely material delivery, managing inventory levels to meet production needs while minimizing costs, selecting cost-effective transportation modes, ensuring warehouse efficiency for receiving and storage, and maintaining quality control over incoming raw materials and components.
What are the main challenges associated with outbound logistics?
Major outbound logistics challenges involve accurate and efficient order fulfillment, optimizing the distribution network for cost and service levels, providing excellent customer service and meeting delivery expectations, managing complexities of last-mile delivery, and handling product returns and reverse logistics processes effectively.
Why is optimizing inbound and outbound logistics important for businesses?
Efficient inbound and outbound logistics operations are crucial for cost-effectiveness by reducing transportation, inventory, and handling costs. They enhance customer satisfaction through reliable, timely deliveries. Optimized logistics enable better inventory management, operational efficiency, competitive advantages, sustainability by lowering environmental impact, and effective risk management against supply chain disruptions.
How can Locus’s dispatch management solution help streamline inbound and outbound logistics?
Locus’s dispatch management software optimizes inbound logistics through seamless supplier coordination, real-time shipment visibility for timely raw material deliveries, and efficient warehouse operations. For outbound, it automates order processing, provides advanced route optimization to minimize costs and delivery times, offers real-time tracking for punctual deliveries, and ensures superb last-mile optimization with dynamic routing, load matching, and accurate ETAs – ultimately driving customer satisfaction. By leveraging this solution, businesses can holistically enhance inbound/outbound efficiency, cut costs, and improve the delivery experience.
Related Tags:

General
White Glove Delivery: Benefits, Key Features & Use Cases
Key Takeaways The tremendous growth of e-commerce has redefined the meaning of luxury among consumers worldwide. It is no longer defined by the monetary value of goods but by the unique, exclusive experience associated with buying something. In e-commerce, this luxury experience is characterized by convenience, speed and some kind of emotional fulfillment. While the […]
Read more
General
What Is Order Fulfillment? Process, Strategies & Tips [2025]
What is order fulfillment? Learn how the process works, why it matters, and how to streamline it with best practices and how to improve with tools like Locus.
Read moreInsights Worth Your Time
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Stay up to date with the latest marketing, sales, and service tips and news
Inbound vs Outbound Logistics: Key Differences in 2025